Blanks and samples show similar RFU values in fluorescence intensity measurements
How to choose the correct excitation and emission wavelengths for fluorescence measurements
1. Usual root causes
If the excitation and emission spectra overlap, you will not actually detect the fluorescence emitted by samples but rather the light coming from the excitation source. This light is very intense and will be brighter than the sample fluorescence.
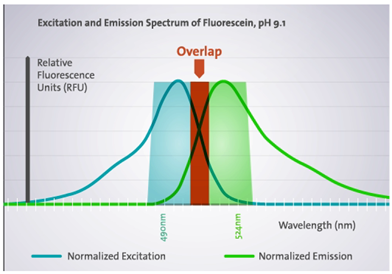
3. Typical solution
Select a suitable filter/wavelength pair for a fluorescent dye:
• Obtain the excitation and emission maxima from the dye’s data sheet or literature.
• Select filters/wavelengths with wavelength properties (wavelength (WL) + bandwidth (BW)) covering the excitation or emission maxima. Depending on the hardware configuration, monochromators can have fixed or adjustable bandwidths.
• Check the filter/wavelength selection for spectral overlap using the following formula: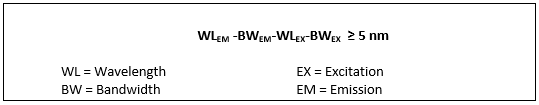
We recommend at least 5 nm separation between the upper end of excitation spectral range (WLEX+BWEX) and the lower end of the emission spectral range (WLEM-BWEM).
• Evaluate and validate the selected filters/wavelengths for your specific assay and use.
Example: fluorescein (pH 9.1)
· Excitation maximum: 492 nm
· Emission maximum: 513 nm
Measurement with filters:
· Recommended excitation filter: 485 nm (20 nm)
· Recommended emission filter: 535 nm (25 nm)
535 – 25 – 485 – 20 = ≥5 nm
The recommended filters for fluorescein cover the respective maxima (excitation and emission) and show the recommended minimal spectral distance of 5 nm.
This also applies to measurements with monochromator (the following example is for the Infinite® 200 PRO)
· Excitation wavelength: 490 nm (9 nm)
· Emission filter: 524 nm (20 nm)
524 – 20 – 490 – 9 = ≥5 nm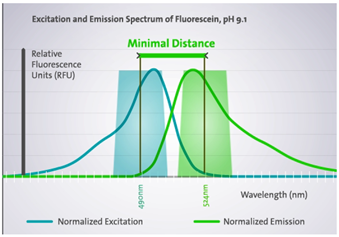
The recommended filters for fluorescein cover the respective maxima (excitation and emission),and show the recommended minimal spectral distance of 5 nm.
3. Next Steps:
If the issue cannot be resolved:
• Note your instrument serial number.
• Create a service request and include the serial number.
Further Help
Link to Tecan Product Page:
401817-014