Keywords:
By Oliver Schmidt
Measuring sIL-2 receptor: a key biomarker for immune activation
The measurement of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) levels in serum or plasma has become an important tool to evaluate immune activation in adults.1 Elevated levels of sIL-2R are typically found in patients with conditions that involve an ongoing immune response.2-6 Reliable sIL-2R ELISA kits for research use are already available. However, the widespread adoption of sIL-2R ELISA in the clinic depends on the development of IVDR-compliant kits. This article describes an open IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kit that can be adapted to different automation platforms.
.png?width=4000&height=2284&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(36).png)
Around 90% of sarcoidosis patients have lung symptoms, with elevated sIL-2R levels indicating immune activation. Tecan’s IVDR sIL-2R kit can be used to measure this diagnostic marker.
How do I know if my lab needs sIL-2R ELISA assays?
To decide whether your lab needs sIL-2R ELISA assays, you or your team may appreciate a more in-depth understanding of the role of interleukin-2 (IL-2) as a key signaling molecule in the human immune system, and as a disease biomarker for inflammation. If so, we invite you to take a tour of our previous article. Otherwise, read on!
In short, IL-2 regulates the activities of the white blood cells that are responsible for immunity, forming part of the body's natural response to infection, and helping it to discriminate between foreign ("non-self") and "self".1 IL-2 mediates its effects by binding to IL-2 receptors, which are expressed by lymphocytes. On T-cell activation, the soluble form of the interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) is secreted, so elevated concentrations of sIL-2R are found in patients suffering from many conditions that are associated with an ongoing immune response.
This means that sIL-2 receptor levels could hypothetically be used as biomarkers to monitor or predict disease activity and treatment response in many different conditions where high levels of sIL-2R have been proven to be clinically relevant, such as sarcoidosis, multiple sclerosis, biliary cirrhosis, chronic immune activation in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH).2-8
It might therefore be worth considering adding IVDR sIL-2R ELISA assays to your lab's assay portfolio if you either need or would like to evaluate clinical samples that could be linked to various disorders that have an associated immune response, where elevated sIL-2R levels are a dependable biomarker, especially those cited above and elsewhere in the literature.2-8
How do I choose which sIL-2R ELISA assay to use?
Once you have determined that sIL-2R ELISA may be useful for you and your healthcare practitioner team to set up in the lab, you may like to consider these few simple questions before making your final decision as to which kits to use, and what degree of automation you may need.
1. Are you working in research or diagnostics?
Research Use Only (RUO) ELISA kits are already available for measuring sIL-2R levels, including the Tecan soluble Interleukin-2-Receptor ELISA - RUO kit. Indeed, Tecan is well-established in the immunoassay field, with an impressive 40-year legacy.
However, if your lab is working with clinical samples to deliver diagnostic results, any kit used must comply with additional national and international regulations. For example, in the European Union, kits used for clinical diagnostics must conform to Regulation (EU) 2017/746 for in vitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDR). In this case, we would recommend that you try the Tecan IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kit, which is also registered with the MHRA (Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency, UK).
Finally, it is recommended that whatever kit you decide to use, it should be calibrated against an international reference standard. Both the Tecan RUO and IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kits come ready-calibrated against the non-WHO reference material NIBSC 97/600.
2. Do you need to automate your sIL-2R analysis?
When starting out with sIL-2R analysis, you may only require enough capacity to run up to 10s of samples per day or week. In this case, manual ELISA may suffice. If you have more samples, would like to minimize the element of human error, or simply need to run multiple dilutions of your samples simultaneously, you may appreciate the availability of automation.
There are closed automated systems available for sIL-2R analysis. However, these may not be economically viable if you are simply looking to add a few sIL-2R assays to your portfolio, or if you have a variable number of samples from week to week.
The most cost-efficient way to add sIL-2R ELISA assays into the mix is to use so-called “open system” kits, which can be easily adapted to different automated systems. Both of the Tecan sIL-2R ELISA kits have readily available protocols (scripts) for systems such as the Freedom EVOlyzer®, ThunderBolt® and DSX®, amongst others.
3. Does your sIL-2R ELISA kit meet the minimum criteria?
Both the Tecan sIL-2R ELISA RUO and sIL-2R ELISA IVDR kits meet the previously described characteristics for sIL-2R measurement:
- All kit reagents are ready-to-use – no dilution necessary
- Include ready-to-use, standard-curve reagents – no stock standard to dilute
- Kit ready-calibrated against NIBSC 97/600 Standard Preparation
- Internal kit controls provided
- Easily automatable
A variety of soluble sIL-2R ELISA assays have a measuring range of up to 10,000 – 20,000 pg/mL.9 This is based on a standard serum dilution of ~1:5, with further dilutions enabling quantification of higher sIL-2R levels. In clinical practice, laboratories may need to use different criteria for determining the upper limit of normal (cut-off) for sIL-2R levels, and the corresponding dilutions, as these may vary by several logs, and will depend very much on the individual patient and their disease status.
4. How do the previous Tecan IVDD kits and IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kits compare?
Figure 1 demonstrates that the IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kit results correlate extremely well with those from the IVDD sIL-2R ELISA kit (r=0.98) and that the results are comparable, robust, and reproducible between the two kits.
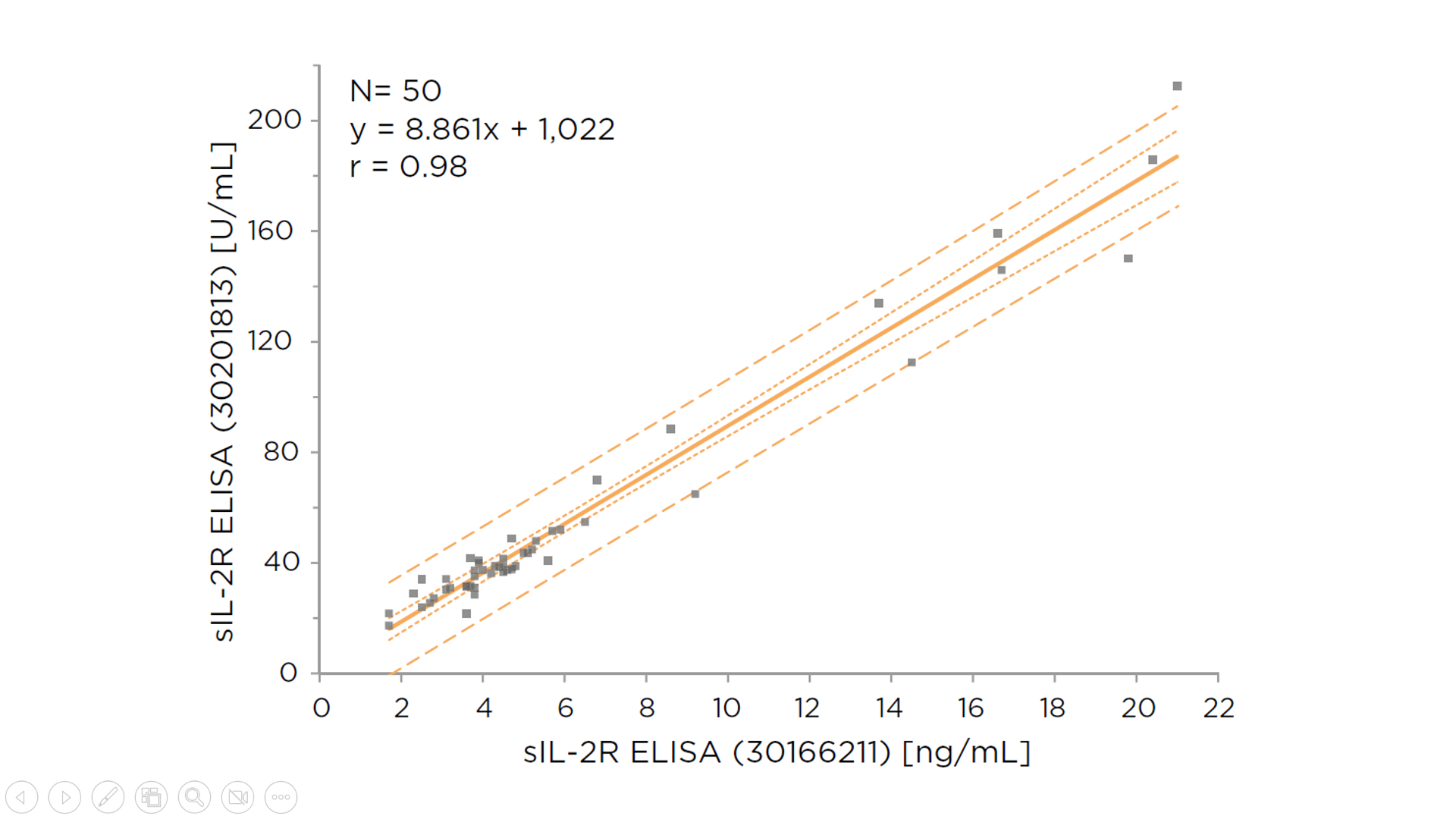
Figure 1. Comparison of Tecan IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kit (y-axis) with sIL-2R ELISA IVDD kit (x-axis). A strong correlation was observed (r=0.98).
In addition, an externally conducted blinded test demonstrated that the Tecan IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kit results correlated extremely well (r=0.98) with those for a similar IVDD device (Fig. 2).
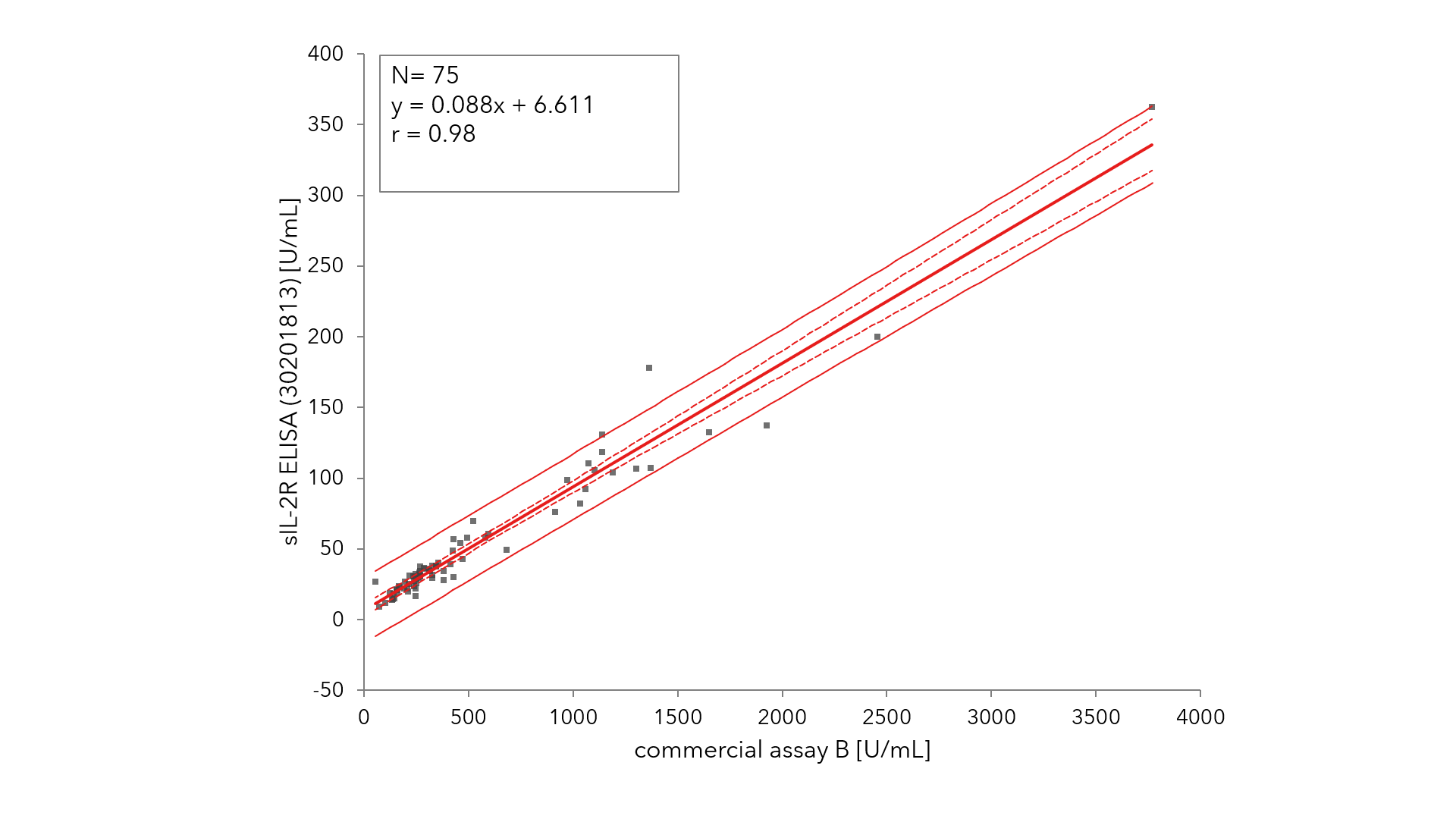
Figure 2: Results from the open system Tecan IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kit correlate well with those from a closed competitor IVD system (r=0.98, Tecan internal data)
5. What case studies can you share for the Tecan sIL-2R ELISA kits?
Changes in the concentration of serum sIL-2R are related to clinical changes, correlating well with changes in pulmonary function parameters and radiological abnormalities in interstitial lung disease (ILD).9-13 The serial measurement of serum sIL-2R during disease follow-up has also proven useful in assessing the evolution of disease activity in sarcoidosis and determining treatment, over both the short and long term.9-13 A compelling illustration of this can be seen in this webinar, given by Dr. Bob Meek (St. Antonius Hospital, NL).
In these studies, the availability of a reproducible and robust sIL-2R ELISA assay has been critical in the follow-up of patients with interstitial lung disease, particularly that caused by sarcoidosis. The team needed a robust, reproducible, and above all, stable assay that would allow them to monitor ILD patients and compare their long-term results, often over a considerable number of years. For example, some patients may have their symptoms managed for over a decade, at which point they could suddenly present with a flare-up of their chronic disease, manifesting with a vastly elevated sIL-2R level, along with other clinical symptoms. In conclusion, the Tecan sIL-2R kit ensures the successful monitoring of ILD patients over time, which is crucial to long-term disease management.
Setting up sIL-2R ELISA assays in your lab: the next steps
For sIL-2R measurement to negotiate the bold move from research into the clinic, it was essential to develop a reliable IVDR-compliant sIL-2R ELISA assay suitable for both small-scale manual and larger-scale automated testing. In developing the IVDR sIL-2R ELISA kit, Tecan has secured the future for this critical biomarker, celebrating its coming of age in the monitoring of inflammatory disease.
Ready to add sIL-2R assays to your portfolio? Follow the promotions for the Tecan sIL-2R ELISA kits here.
References
1. Liao, W., Lin, J. X., & Leonard, W. J. (2011). IL-2 family cytokines: new insights into the complex roles of IL-2 as a broad regulator of T helper cell differentiation. Current opinion in immunology, 23(5), 598–604.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21889323/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2011.08.003
2. Thi Hong Nguyen, C., Kambe, N., Kishimoto, I., Ueda-Hayakawa, I., & Okamoto, H. (2017). Serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor level is more sensitive than angiotensin-converting enzyme or lysozyme for diagnosis of sarcoidosis and may be a marker of multiple organ involvement. The Journal of dermatology, 44(7), 789–
797.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28295528/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.13792
3. Peerlings, D., Mimpen, M., & Damoiseaux, J. (2021). The IL-2–IL-2 receptor pathway: Key to understanding multiple sclerosis. Journal of Translational Autoimmunity, 100123.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35005590/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100123
4. Barak, V., Selmi, C., Schlesinger, M., Blank, M., Agmon-Levin, N., Kalickman, I., Gershwin, M. E., & Shoenfeld, Y. (2009). Serum inflammatory cytokines, complement components, and soluble interleukin 2 receptor in primary biliary cirrhosis. Journal of autoimmunity, 33(3-4), 178–182.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19846277/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2009.09.010
5. Litzman, J., Nechvatalova, J., Xu, J., Ticha, O., Vlkova, M., & Hel, Z. (2012). Chronic immune activation in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is associated with elevated serum levels of soluble CD14 and CD25 but not endotoxaemia. Clinical and experimental immunology, 170(3), 321–332.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23121673/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04655.x
6. Lin, M., Park, S., Hayden, A., Giustini, D., Trinkaus, M., Pudek, M., Mattman, A., Schneider, M., & Chen, L. (2017). Clinical utility of soluble interleukin-2 receptor in hemophagocytic syndromes: a systematic scoping review. Annals of hematology, 96(8), 1241–1251.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28497365/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-2993-y
7. Durda, P., Sabourin, J., Lange, E. M., Nalls, M. A., Mychaleckyj, J. C., Jenny, N. S., Li, J., Walston, J., Harris, T. B., Psaty, B. M., Valdar, W., Liu, Y., Cushman, M., Reiner, A. P., Tracy, R. P., & Lange, L. A. (2015). Plasma Levels of Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor α: Associations With Clinical Cardiovascular Events and
Genome-Wide Association Scan. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology, 35(10), 2246–2253.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26293465/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305289
8. Karim, A. F., Eurelings, L., Bansie, R. D., van Hagen, P. M., van Laar, J., & Dik, W. A. (2018). Soluble Interleukin-2 Receptor: A Potential Marker for Monitoring Disease Activity in IgG4-Related Disease. Mediators of inflammation, 2018, 6103064.
PubMed ID: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5854105/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6103064
9. Damoiseaux J. (2020). The IL-2 - IL-2 receptor pathway in health and disease: The role of the soluble IL-2 receptor. Clinical immunology (Orlando, Fla.), 218, 108515.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32619646/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2020.108515
10. Milou C. Schimmelpennink MD, Adriane D.M. Vorselaars MD, PhD, Jan C. Grutters MD. Sarcoidosis: A Clinician's Guide (2019), Chapter 19 - Biomarkers in Sarcoidosis. Pages 219-238.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25496652/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-54429-0.00019-7
11. Vanmaris, R. M. M., & Rijkers, G. T. (2017). Biological role of the soluble interleukin-2 receptor in sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis, vasculitis, and diffuse lung diseases : official journal of WASOG, 34(2), 122–129.
PubMed ID: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7170137/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36141/svdld.v34i2.5369
12. Schimmelpennink, M. C., Quanjel, M., Vorselaars, A., Wiertz, I., Veltkamp, M., Van Moorsel, C., & Grutters, J. C. (2020). Value of serum soluble interleukin-2 receptor as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in sarcoidosis. Expert review of respiratory medicine, 14(7), 749–756.
PubMed ID: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32248706/
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/17476348.2020.1751614
13. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/sarcoidosis/ Accessed 4 April 2024
Keywords:
About the author

Oliver Schmidt
Oliver Schmidt is product manager for research reagents, neurodegeneration, and bone and mineral products at TECAN-IBL in Hamburg with more than 10 years’ experience in bringing these products to the Life Science and academic community. He studied Environmental Engineering at the Technical University of Hamburg-Harburg and joined TECAN-IBL in 2005.